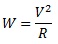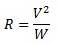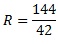As always, I like to encourage others to make things and I often get asked "What size wire should I use for a particular length polystyrene hot wire cutter". My answer is that I do not know because I don't know what power supply you have, but I generally recommend starting with the power supply and then choosing the wire that will work best with the power available.
The very next question would then be "What power supply should I use?" And the answer is generally" the biggest thing you have but it depends on how long and how thick you want the wire".
Oh dear, at this stage what started off as trying to be help just adds to the bewilderment of the customer.
So I'm going to try and put something together on this page that will help you all to make the best decisions based on the facts which I hope will keep you all that little bit safer.
What Power supply?
The lowest power needed for the range of wire that we sell is around 40 watts which would power a wire approx 100mm. That wire would be very thin at 0.2mm diameter but it would be ideal for thin cuts but it may break.
The same power supply could also power a wire 1500mm long, this wire would be much thicker at 0.8mm but it would not be ideal for thin detailed cuts although it will not break.
So a compromise of 1000mm long using a 0.5mm wire could be good for some applications.
Or possibly 400mm using 0.4mm wire.
So you should start with a power supply capable of at least 40 watts.
What are Watts?
The power of a power supply is measured in watts, but not all power supplies state the wattage but it can be calculated very easily. The power supply should state the output voltage and current, something similar to 12v and 3.5 Amps. The current can also be shown as 3.5A.
If we multiply these 2 numbers together we get the wattage, so 12v X 3.5A = 42 watts.
What size wire to use?
So we know what power supply we have, now we need to check if it will be ok for your needs and work out exactly what wire will be needed by using the following formula:
The very next question would then be "What power supply should I use?" And the answer is generally" the biggest thing you have but it depends on how long and how thick you want the wire".
Oh dear, at this stage what started off as trying to be help just adds to the bewilderment of the customer.
So I'm going to try and put something together on this page that will help you all to make the best decisions based on the facts which I hope will keep you all that little bit safer.
What Power supply?
The lowest power needed for the range of wire that we sell is around 40 watts which would power a wire approx 100mm. That wire would be very thin at 0.2mm diameter but it would be ideal for thin cuts but it may break.
The same power supply could also power a wire 1500mm long, this wire would be much thicker at 0.8mm but it would not be ideal for thin detailed cuts although it will not break.
So a compromise of 1000mm long using a 0.5mm wire could be good for some applications.
Or possibly 400mm using 0.4mm wire.
So you should start with a power supply capable of at least 40 watts.
What are Watts?
The power of a power supply is measured in watts, but not all power supplies state the wattage but it can be calculated very easily. The power supply should state the output voltage and current, something similar to 12v and 3.5 Amps. The current can also be shown as 3.5A.
If we multiply these 2 numbers together we get the wattage, so 12v X 3.5A = 42 watts.
What size wire to use?
So we know what power supply we have, now we need to check if it will be ok for your needs and work out exactly what wire will be needed by using the following formula:
The W is the watts of your power supply.
The V squared is the power supplies output voltage multiplied by itself.
The R is the total resistance of the hot wire that you will require.
So we can manipulate this formula to show it another way:
The V squared is the power supplies output voltage multiplied by itself.
The R is the total resistance of the hot wire that you will require.
So we can manipulate this formula to show it another way:
If we use the power supply in our example earlier, this would equate to:
Which gives us a resistance of 3.43 Ω
Resistance is measured in Ohms (Ω) so the total resistance of your nichrome wire should be approx 3.43 Ohms.
Now we have the Total Resistance what next?
On our nichrome wire page we have added the resistance (ohms) per metre next to each wire.
So lets say we want our hot wire length to be 100mm long which is 0.1 of a metre and we know the total resistance needs to be 3.43 Ω.
So if we multiply our 3.43 Ω by 10 then we should get the resistance we need per metre.
So that would equal 34.3 Ω, now go to the nichrome wire page and look for a wire that is the closest to 34.3 Ω per metre.
You should have found that the 0.2mm wire is the closest at 34.4 Ω per metre.
What Did We Learn?
If you followed this from the top of the page then hopefully you would have learnt the following:
It's important to know how long you need your hot wire to be, the shorter the better.
Calculate your power supplies power in watts before you buy one.
Using the wattage, calculate the total resistance of the nichrome wire that is needed.
Using the total resistance calculate the resistance per metre.
Using the resistance per metre check what or if a suitable nichrome wire can be found on our website.
The information on this page is designed to get you in the ball park of getting the correct power supply matched to the correct wire and length, to optimize the heat of your nichrome wire you will have to shorten or lengthen the wire (although not by much) to adjust the heat to suit your needs, or alternatively connect a dimmer switch (the type used to adjust your mains room lights), either way remember that the wire does not need to be red hot, being red hot is a disadvantage so adjust the length to avoid this.
If after all the calculations you are unable to find a suitable wire or the wire is too thin or thick then either alter the length you require of your wire or use another power supply and recalculate.
I don't like formulas, is there an easier way?
My local shop doesn't have the diameter in mm?
What's the difference between AWG and SWG wire sizes?
OK, so I here what you are saying and I've put together an excel sheet that will calculate everything for you and tell you what the best wire to use in both metric and imperial and also in both the AWG and SWG wire gauges.
You can download the excel file that matches your version of excel below:
These files are safe and do not have any advertising or viruses, however your version of excel may warn you about downloading files from the internet. If you are not sure what version then starting at the top click on one until it works for you.
Resistance is measured in Ohms (Ω) so the total resistance of your nichrome wire should be approx 3.43 Ohms.
Now we have the Total Resistance what next?
On our nichrome wire page we have added the resistance (ohms) per metre next to each wire.
So lets say we want our hot wire length to be 100mm long which is 0.1 of a metre and we know the total resistance needs to be 3.43 Ω.
So if we multiply our 3.43 Ω by 10 then we should get the resistance we need per metre.
So that would equal 34.3 Ω, now go to the nichrome wire page and look for a wire that is the closest to 34.3 Ω per metre.
You should have found that the 0.2mm wire is the closest at 34.4 Ω per metre.
What Did We Learn?
If you followed this from the top of the page then hopefully you would have learnt the following:
It's important to know how long you need your hot wire to be, the shorter the better.
Calculate your power supplies power in watts before you buy one.
Using the wattage, calculate the total resistance of the nichrome wire that is needed.
Using the total resistance calculate the resistance per metre.
Using the resistance per metre check what or if a suitable nichrome wire can be found on our website.
The information on this page is designed to get you in the ball park of getting the correct power supply matched to the correct wire and length, to optimize the heat of your nichrome wire you will have to shorten or lengthen the wire (although not by much) to adjust the heat to suit your needs, or alternatively connect a dimmer switch (the type used to adjust your mains room lights), either way remember that the wire does not need to be red hot, being red hot is a disadvantage so adjust the length to avoid this.
If after all the calculations you are unable to find a suitable wire or the wire is too thin or thick then either alter the length you require of your wire or use another power supply and recalculate.
I don't like formulas, is there an easier way?
My local shop doesn't have the diameter in mm?
What's the difference between AWG and SWG wire sizes?
OK, so I here what you are saying and I've put together an excel sheet that will calculate everything for you and tell you what the best wire to use in both metric and imperial and also in both the AWG and SWG wire gauges.
You can download the excel file that matches your version of excel below:
These files are safe and do not have any advertising or viruses, however your version of excel may warn you about downloading files from the internet. If you are not sure what version then starting at the top click on one until it works for you.
| nichrome_wire_calculator_excel_2010_v2.xlsx | |
| File Size: | 14 kb |
| File Type: | xlsx |
| nichrome_wire_calculator_excel_97-2003_v2.xls | |
| File Size: | 36 kb |
| File Type: | xls |
| nichrome_wire_calculator_excel_5-95_v2.xls | |
| File Size: | 25 kb |
| File Type: | xls |
Feel free to download and use this calculator, if you come across an error in the file or in anything on this website or just want to ask more questions then please email us at [email protected]
Nichrome Wire Voltage/Current Needs for a successful polystyrene cut
These are actual results that may help you choose the correct wire
I have been meaning to collate & publish this data for a while but when I finally got around to it I found our variable DC 30v-5A power supply didn't really have the necessary grunt to complete the table, however below you will find the results of what I've managed to get so far.
Instead of using the American or Standard wire gauge which causes confusion, I've simplified it by putting the wire size in mm.
Since we created the table below we have designed the downloadable calculator tool above to help you choose the right size nichrome wire.
Wire size Current Voltage mm Comment on polystyrene cut
0.2 0.65 12 500 cold cut 0.2 0.8 12 400 warm cut 0.2 1.05 12 300 warmer cut 0.2 1.24 12 250 ok 0.315 1.56 12 500 warm cut 0.315 1.89 12 400 ok 0.315 2.0 8 250 ok 0.4 2.66 12 500 ok 0.4 3.24 12 400 perfect 0.5 3.7 12 500 almost ok 0.5 4.55 12 400 perfect 0.63 5.0 9.6 500 warm cut 0.63 5.0 7.6 400 warmer cut 0.63 5.0 5.6 300 cold cut
Instead of using the American or Standard wire gauge which causes confusion, I've simplified it by putting the wire size in mm.
Since we created the table below we have designed the downloadable calculator tool above to help you choose the right size nichrome wire.
Wire size Current Voltage mm Comment on polystyrene cut
0.2 0.65 12 500 cold cut 0.2 0.8 12 400 warm cut 0.2 1.05 12 300 warmer cut 0.2 1.24 12 250 ok 0.315 1.56 12 500 warm cut 0.315 1.89 12 400 ok 0.315 2.0 8 250 ok 0.4 2.66 12 500 ok 0.4 3.24 12 400 perfect 0.5 3.7 12 500 almost ok 0.5 4.55 12 400 perfect 0.63 5.0 9.6 500 warm cut 0.63 5.0 7.6 400 warmer cut 0.63 5.0 5.6 300 cold cut
If you like our site then please click on the Facebook icon at the top right of this page, thank you.
For more information you can email us via our Contact Us page.